

Lifestyle
Ethereum Price USDT Analysis: Bitget Data Reveals Market Momentum
Ethereum is one of the most used cryptocurrencies. Ethe [ ]

Technology
How to Track Your Monopoly GO Order on U4GM
Purchasing digital products online is thrilling, but it [ ]

Lifestyle
The Business Case for Sourcing Crewneck Sweaters Wholesale
Crewneck sweaters remain a mainstay in fashion across d [ ]
Lifestyle
How Gauth Can Assist You in Locating the Best American Bully Captions
It is always a joy to try and capture the loyalty of yo [ ]

Industry
What Diverse Range Of Applications Does ASTM A53 ERW Pipe Support In Modern Infrastructure Development?
In the bustling tapestry of modern society, the importa [ ]
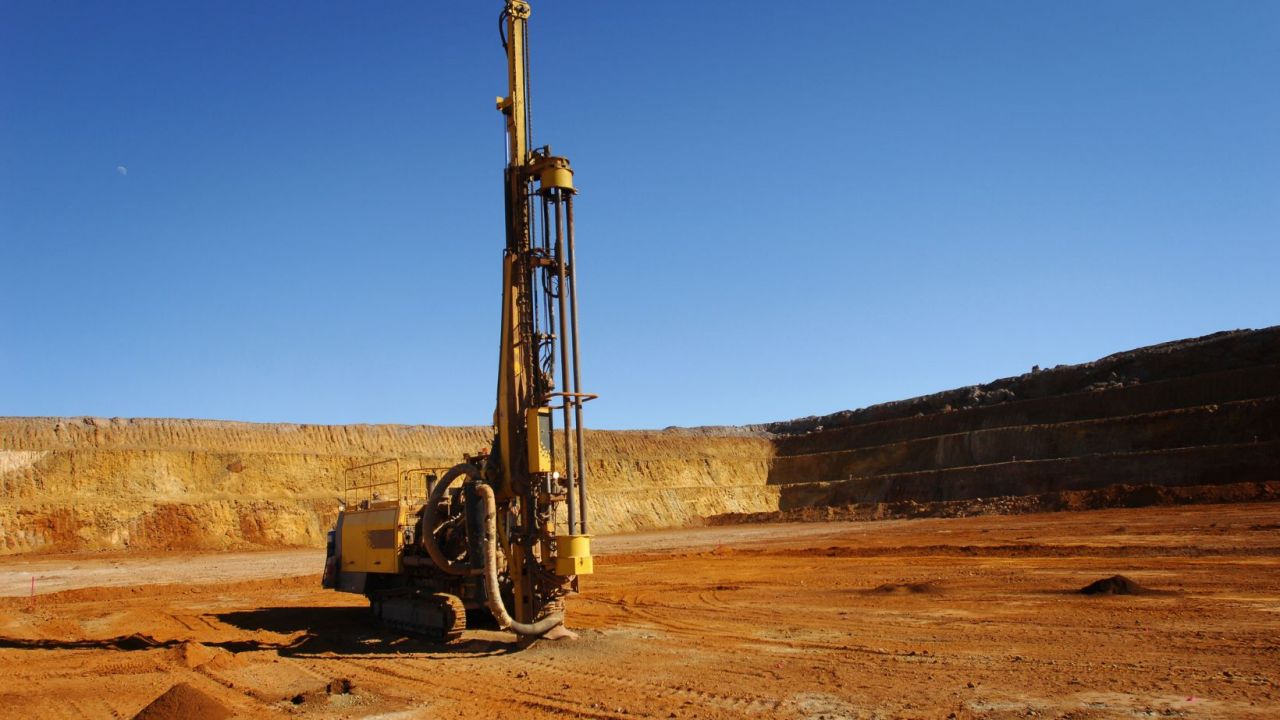

Industry
Top 8 Oil Rig Tools and Equipment Used in Oil Drilling Process
The Earth s crust spews a valuable resource, crud [ ]
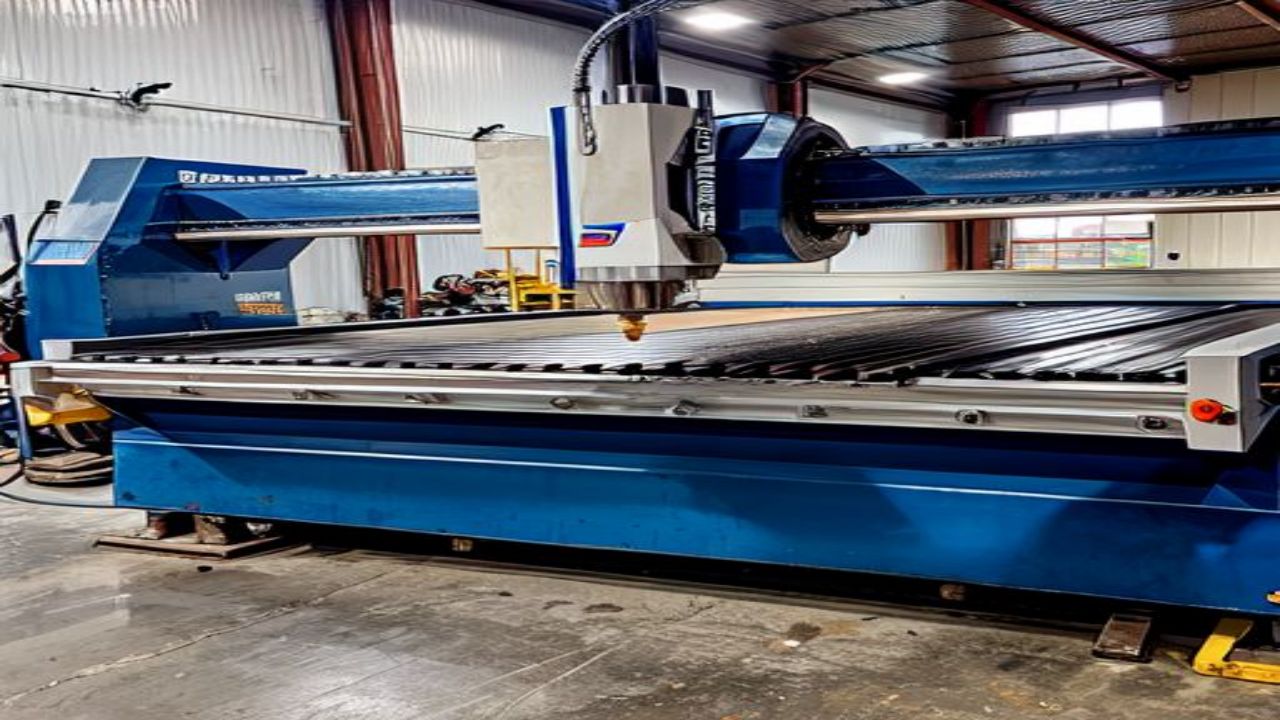

Industry
CNC Machining vs. Traditional Manual Techniques: A Battle of Quality and Efficiency
In the realm of manufacturing, two distinct approaches [ ]
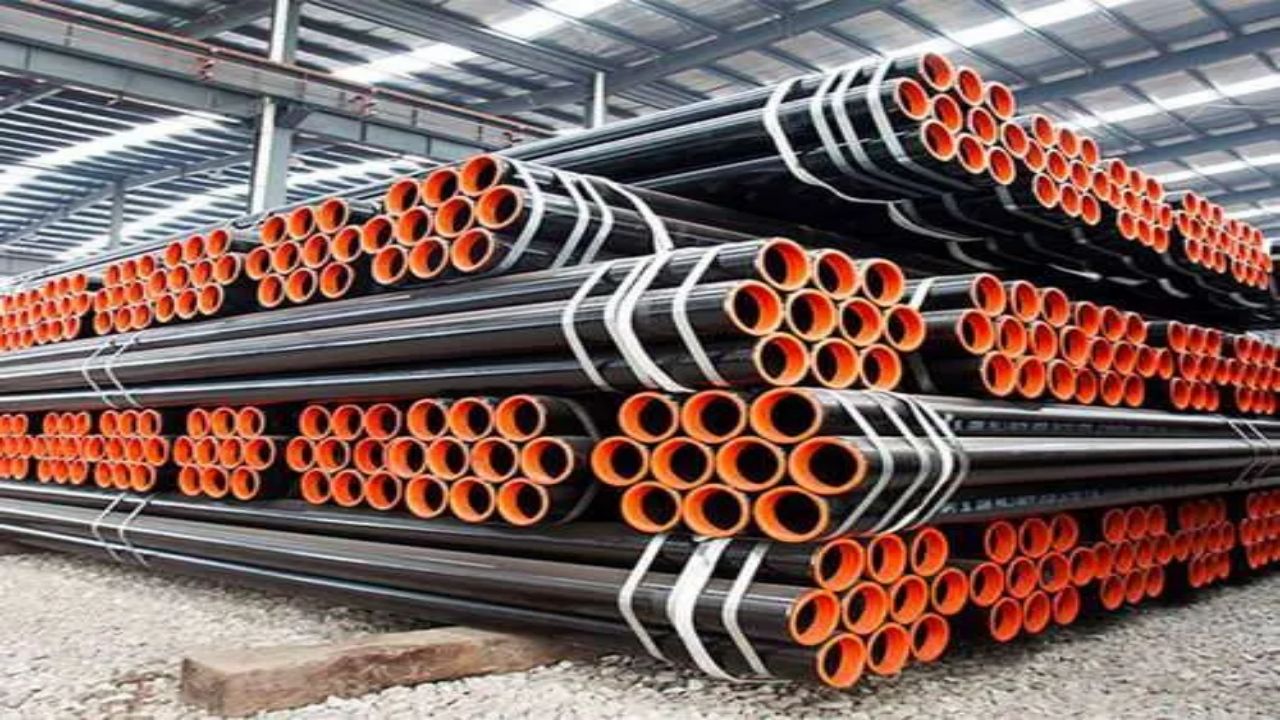

Industry
The Impact of Technological Advancements on Line Pipe Manufacturing
Reagrdless of the industry, technological advancements [ ]

Industry
Mastering the Art of Trencher Teeth Installation and Adjustment: An Indispensable Guide
The prowess of any trenching machine is heavily reliant [ ]

Industry
Stretch Wrap Manufacturer: A Comprehensive Guide to Product Types and Applications
Stretch wrap, also known as stretch film or pallet wrap [ ]

Industry
Custom Forging vs. Standard Components: Why Choose Customization?
In various industries, the choice between custom forgin [ ]

Industry
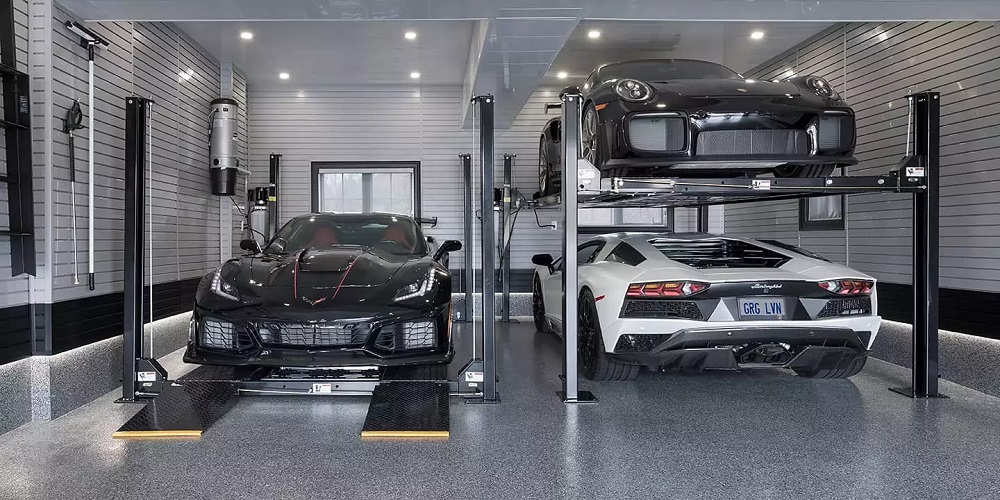
Price structure for car lift installation
Heavy machines, plants, and equipment are integral part [ ]
